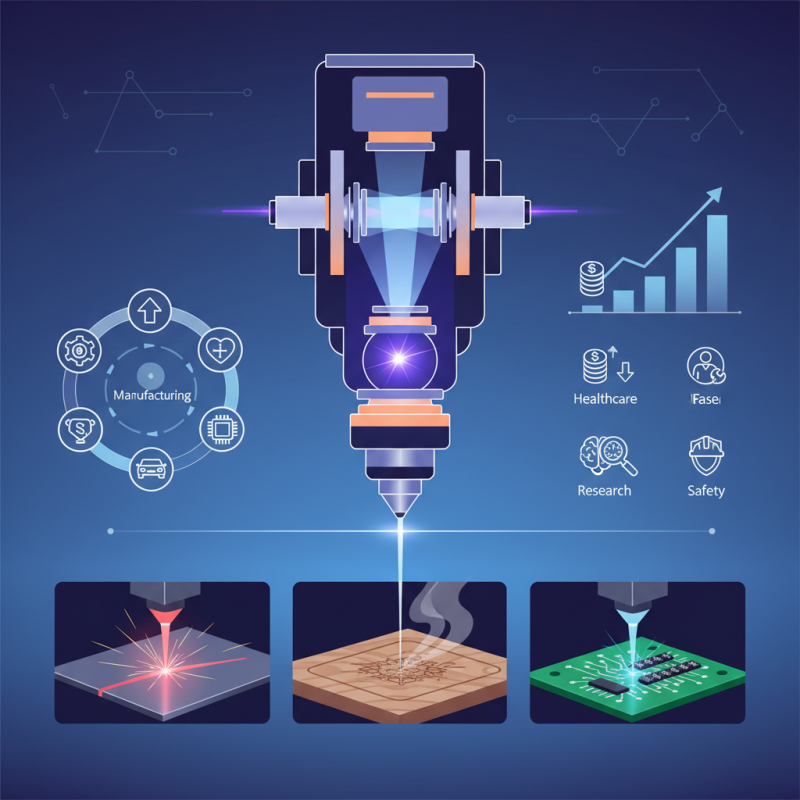
The Laser Head is a crucial component in various industries, impacting manufacturing and technology. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global laser industry is projected to reach $15.7 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by advancements in laser technology and increasing applications in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and electronics.
A Laser Head utilizes focused light beams to perform tasks like cutting, engraving, and marking. These processes are highly precise and efficient. For instance, laser cutting can achieve tolerances of ±0.1 mm. However, the technology isn't without challenges. Operators may face difficulties in optimizing settings for different materials, leading to inconsistent results.
Moreover, as industries adopt laser technology, the demand for skilled technicians rises. Training is essential for maintaining quality and safety standards. There is also a need for more research on the long-term effects of laser exposure on workers. Thus, while the Laser Head offers remarkable benefits, careful consideration is necessary for its implementation and use.

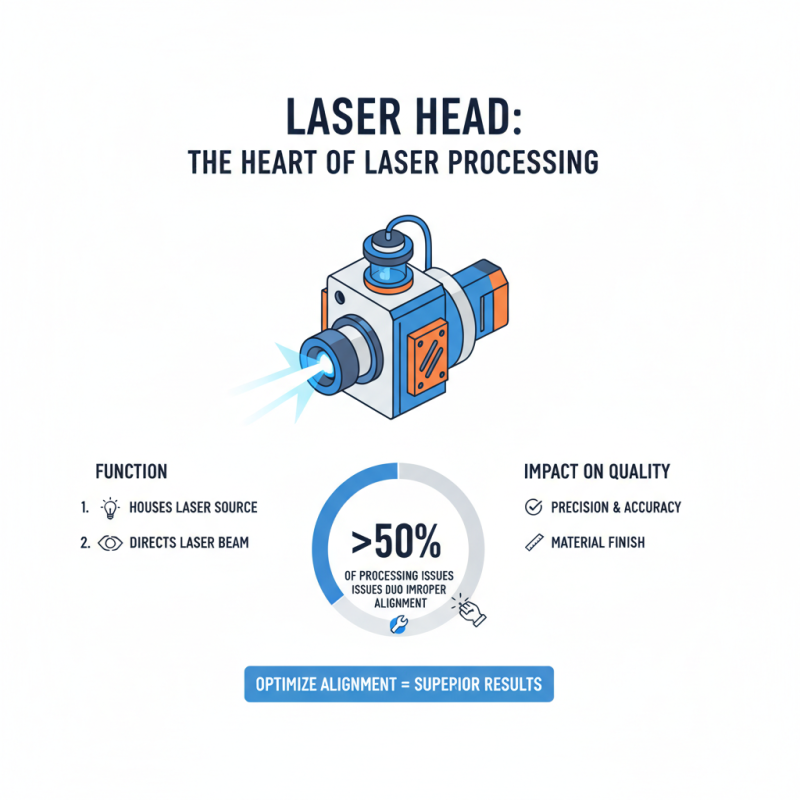
A laser head is a critical component in laser cutting and engraving systems. It houses the laser source and optics necessary for directing the beam to the work material. The efficiency of a laser head can greatly affect the quality of the final product. According to a recent industry report, more than 50% of the processing issues stem from improper laser head alignment.
Laser heads come in various designs, each optimized for specific tasks. Some are designed for precision cutting, while others excel in engraving. A well-calibrated laser head can provide cuts with thicknesses as fine as 0.1mm, ensuring intricate designs are accurately produced. However, it's important to note that wear and tear on the optics can lead to diminished performance, requiring regular maintenance and inspection.
Tip: Regularly check and clean the laser lens to prevent performance degradation. A dirty lens can scatter the laser beam, leading to inconsistent results. Another aspect to consider is the cooling system. Overheating can damage the laser head and affect its lifespan.
Maintaining equipment is essential for optimal operation. Even minor misalignments can lead the laser to cut inaccurately. Users should stay informed on best practices to avoid these common pitfalls. Seek feedback periodically; it can provide insights into potential improvements in your setup.
A laser head is a vital component in laser systems. Understanding its key components helps in grasping how it functions. Each part plays a specific role in the process of laser generation.
The primary component is the laser medium. This medium, often a gas, liquid, or solid, is where the laser light is produced. Energy excites the atoms or molecules in the medium, causing them to emit photons. These photons are the building blocks of laser light. In addition, a pair of mirrors is essential. One mirror is highly reflective, while the other is partially transparent. This setup allows the light to bounce back and forth, amplifying it.
Cooling systems are also critical. They prevent overheating, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Many people overlook this essential part. Without proper cooling, the laser head may malfunction. Furthermore, alignment systems maintain the precision of the laser beam. Misalignment can lead to inefficiency and reduced quality. Understanding these components reveals the complexity behind a seemingly simple tool. Each piece contributes significantly to the overall function, emphasizing the importance of careful design and maintenance.
A laser head is a crucial component in laser technology. It directs and focuses the beam of light generated by the laser. Understanding its operation begins with the basic principles of laser technology. Lasers produce light through a process called stimulated emission. When atoms are excited by energy sources, they emit photons. These photons then stimulate more atoms to release photons, creating a chain reaction.
This process happens in a medium, often a gas, liquid, or solid. The laser head contains mirrors that amplify this light. One mirror reflects nearly all the light, while the other is partially transparent. This design allows some light to escape as a coherent beam. The emitted light has a very narrow wavelength range. This purity contributes to its effectiveness in various applications, including cutting and engraving.
However, there are challenges in laser operation. The alignment of components must be precise. Even minor misalignments can degrade performance. This makes setup a delicate process. Additionally, safety is a constant concern. Proper shielding and training are necessary to prevent accidents. These details underscore the complexity involved in harnessing laser technology effectively.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A laser head is a component that generates and directs laser beams. |
| Main Components | Includes a laser medium, a power source, and optical elements. |
| Laser Medium | The material that produces laser light, such as gas, liquid, or solid. |
| Operating Principle | Uses stimulated emission to amplify light and produce a coherent beam. |
| Applications | Used in medical procedures, manufacturing, communication, and scientific research. |
| Types of Lasers | Includes CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, diode lasers, and solid-state lasers. |
| Safety Measures | Protective eyewear and proper ventilation are essential for safe operation. |
Laser heads play a crucial role in various industrial applications. In manufacturing, they are often used for cutting materials like metals and plastics. Their precision minimizes waste and enhances production efficiency. The focused beam can slice through thick materials with ease. This ability saves time and reduces operational costs. However, improper use can lead to damage or inconsistent cuts, requiring operators to be skilled.
In addition to cutting, laser heads are essential for welding and engraving. They can create strong welds without added materials. This is vital in industries where structural integrity is key. Engraving with lasers allows for unique designs on products, helping businesses stand out. Nevertheless, achieving the perfect depth and design requires practice and careful calibration. Mistakes happen, and adjustments might be necessary after initial attempts.
Furthermore, the use of laser heads in medical applications is growing. They are employed in surgeries and diagnostics, showcasing their versatility. The precision of lasers can result in less invasive procedures. However, the learning curve in adapting this technology is steep. Not every operator feels comfortable with such equipment initially. Overall, while laser heads offer impressive advantages, they demand careful handling and expertise.
Laser heads play a vital role in precision cutting and engraving processes. However, maintenance and safety considerations are often overlooked. Proper care ensures longevity and optimal performance. Cleanliness is crucial; dust or residue can obstruct laser beams. Regularly inspect lenses and mirrors for damage. According to industry studies, a clean workspace can increase efficiency by up to 25%.
Safety protocols are essential when operating laser heads. Protective eyewear must be worn at all times. The intensity of laser light can cause severe eye damage. Furthermore, ensure that the work area is free from flammable materials. Statistics indicate that improper handling leads to 30% of workplace accidents involving laser equipment.
Training and understanding of laser technology are critical. Many users underestimate the risks associated with laser operations. The consequences of neglect can be dire, resulting in equipment failure or personal injury. Regular training sessions can enhance awareness and improve safety standards significantly. Awareness fosters a culture of safety that benefits everyone involved.