Cladding Technology serves as a crucial element in modern architecture and construction, enhancing aesthetic appeal, energy efficiency, and structural protection. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global cladding market is projected to reach an estimated value of $320 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for durable and energy-efficient building materials. In recent years, the adoption of cladding systems has expanded across various sectors, from residential to commercial properties, emphasizing the technology's versatility and effectiveness in addressing contemporary building challenges.

The benefits of Cladding Technology extend beyond mere aesthetics; it plays a pivotal role in improving energy efficiency, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring the longevity of structures. A study by the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that properly designed cladding systems can reduce heat loss by up to 50%, significantly lowering heating costs and the overall carbon footprint of buildings. Furthermore, the variety of cladding materials available, including wood, metal, brick, and composite options, allows architects and builders to tailor solutions that meet both functional demands and design aspirations, making Cladding Technology an indispensable choice in today’s construction landscape.
Cladding technology refers to the application of an outer layer of material to the building's structure, primarily to enhance its aesthetics, thermal performance, and weather resistance. It acts as a protective barrier, helping to insulate the building while also providing a finished look. The types of cladding materials can vary widely, including metal, wood, brick, and composite options, each offering distinct advantages in terms of durability and maintenance.
Recent developments in building safety regulations, particularly regarding the use of combustible materials, have spurred significant changes in the industry. As the Building Safety Act 2022 introduced stricter guidelines, confusion surrounding acceptable cladding materials has emerged. This has prompted industry associations to clarify the use of various materials and ensure compliance, emphasizing the importance of selecting non-combustible options in certain high-risk buildings. Understanding these regulations is critical for architects and builders to mitigate safety risks and ensure the long-term resilience of their structures.
Cladding technology plays a crucial role in modern construction, primarily by improving a building's durability and energy efficiency. One of the primary benefits of cladding is its ability to protect structures from environmental harm. High-quality cladding materials can resist moisture, wind, and UV radiation, significantly extending the lifespan of the underlying structure. This protective layer minimizes the risk of damage due to weather-related factors, leading to lower maintenance costs and prolonged building integrity.
In addition to durability, cladding also enhances a building's energy efficiency. By providing an additional layer of insulation, cladding can help regulate indoor temperatures, reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems. This not only leads to lower energy bills but also contributes to a more sustainable environment. With various options available, such as insulated panels, wood, metal, and stone, builders can select materials that best fit both aesthetic and functional requirements, further optimizing energy performance.
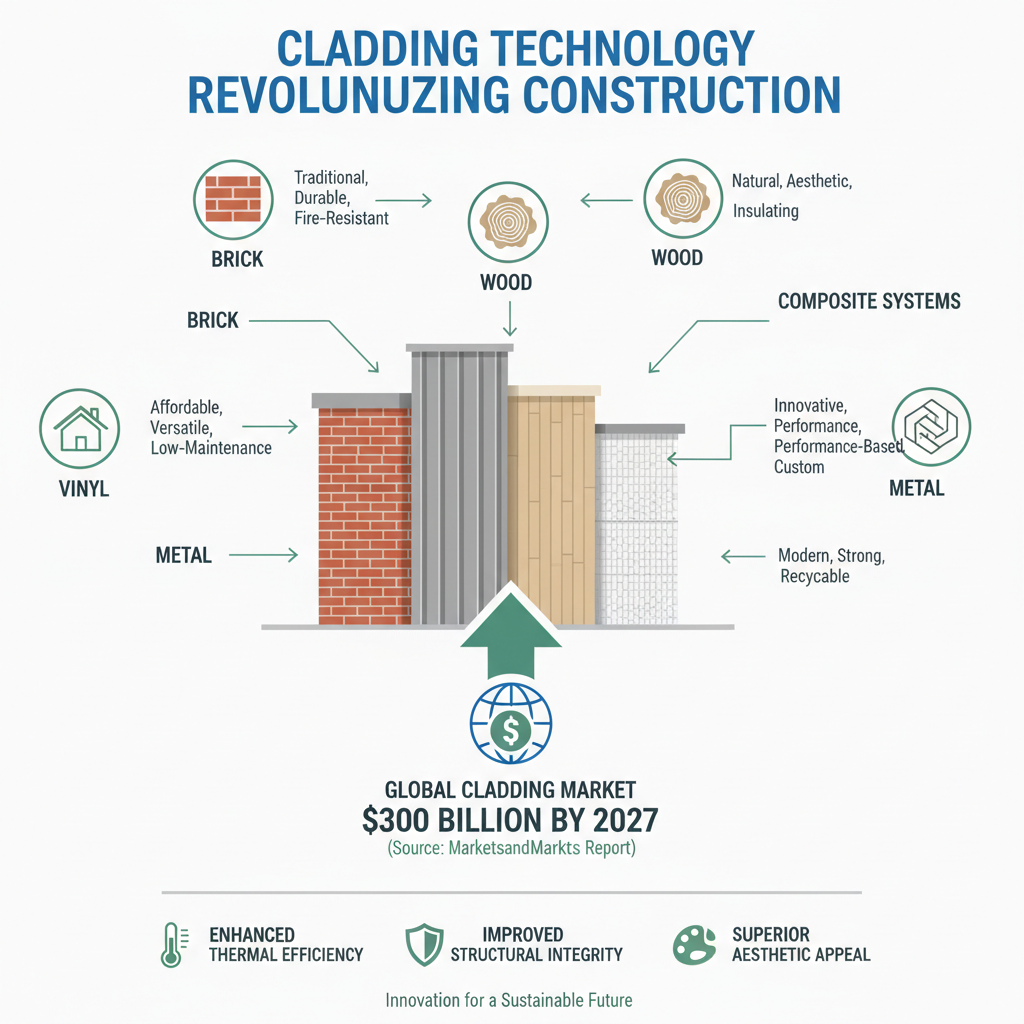
Cladding technology has revolutionized the construction industry, providing not only aesthetic appeal but also enhancing thermal efficiency and structural integrity. Among the diverse options available, the most common cladding materials include brick, vinyl, wood, metal, and composite systems. According to a report by "MarketsandMarkets," the global cladding market is projected to reach $300 billion by 2027, showcasing the increasing popularity and versatility of these materials.
When evaluating cladding materials, it is essential to consider their properties and performance characteristics. For instance, brick cladding is celebrated for its durability and low maintenance, while wood offers a warm, natural appearance but requires more upkeep. Metal cladding, particularly aluminum, has gained traction due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for modern architectural designs. A comparative analysis from "Grand View Research" indicates that vinyl cladding is favored for residential buildings due to its affordability and easy installation, holding a significant market share of 30% in the residential sector alone.
Each material presents unique benefits that can influence project outcomes significantly. The choice depends on factors like budget, climate, and aesthetic preferences, demonstrating the importance of informed decision-making in selecting cladding materials for any construction project.
Cladding technology plays a critical role in enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of both residential and commercial buildings. In residential settings, cladding provides insulation and protects the structure from weather elements. According to a recent report by Smithers Pira, the global cladding market size is projected to reach $300 billion by 2025, indicating a growing recognition of its importance in home construction. Common materials used for residential cladding include wood, vinyl, and fiber cement, each offering unique benefits in terms of cost and durability.
In commercial buildings, cladding serves not only to protect but also to improve energy efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. Studies from the National Institute of Building Sciences highlight that properly chosen cladding can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 20%. This is particularly crucial in urban environments where energy demands are high. Popular choices for commercial cladding materials include metal panels and glass, which provide sleek, modern aesthetics while often maximizing natural light.
Tips: When selecting cladding for your project, consider the local climate and the building’s energy efficiency goals. Additionally, ensure that the chosen materials comply with local building codes and sustainability standards to contribute to overall environmental performance. Engaging with a professional architect or contractor can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific needs.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Benefits | Enhances insulation, reduces energy costs, improves aesthetics, provides protection against weather elements. |
| Types | Vinyl, Wood, Metal, Brick, Composite, Stone. |
| Applications in Residential | Single-family homes, multi-family apartments, housing developments, renovations. |
| Applications in Commercial | Office buildings, retail spaces, industrial warehouses, educational institutions. |
| Sustainability Factors | Recyclable materials, reduced energy consumption, longer lifespans. |
| Installation Considerations | Professional installation recommended, local building codes compliance, moisture management. |
Cladding technology is witnessing transformative industry trends as it adapts to the evolving demands for sustainability, aesthetics, and performance in construction. Recent reports indicate that the global cladding market is projected to reach a value of approximately $260 billion by 2027, driven by innovations that prioritize energy efficiency and environmental impact. Notably, developments in insulated metal panels and eco-friendly materials are gaining traction, aligning with the broader movement towards greener architecture and the reduction of carbon footprints in building practices.
Furthermore, the rise of startups focusing on cladding solutions illustrates the dynamic landscape of the industry. Out of over 4,700 startups identified, 20 are at the forefront of integrating cutting-edge technologies such as smart sensors and augmented reality into cladding systems. These innovations not only enhance building performance but also offer new opportunities for design flexibility and integration with smart building technologies. As these trends continue to evolve, stakeholders in the building materials sector must stay abreast of these developments to leverage advancements that will shape the future of construction.






