In the evolving landscape of advanced manufacturing, "Laser Cladding" has emerged as a pivotal technique for enhancing material performance. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Chen states, “Laser Cladding can transform traditional approaches to surface treatment.” This method effectively combines precise laser energy with additives to improve wear resistance and reduce corrosion. Each application varies, from aerospace to automotive industries, showcasing diverse potential.
While exploring the best Laser Cladding techniques, it’s essential to acknowledge the complexities involved. Each technique uniquely contributes to performance enhancement but is not without its challenges. For example, thermal management during the process can be tricky. A delicate balance between heat input and material properties must be maintained.
Understanding these nuances is key. There’s a risk of over-engineering, where the excitement for advancements may lead to oversight of fundamental principles. Reflexivity is vital in assessing how these techniques can be optimized for real-world applications. As we examine the best practices, a consideration of practical execution will be crucial for successful implementations in various industries.

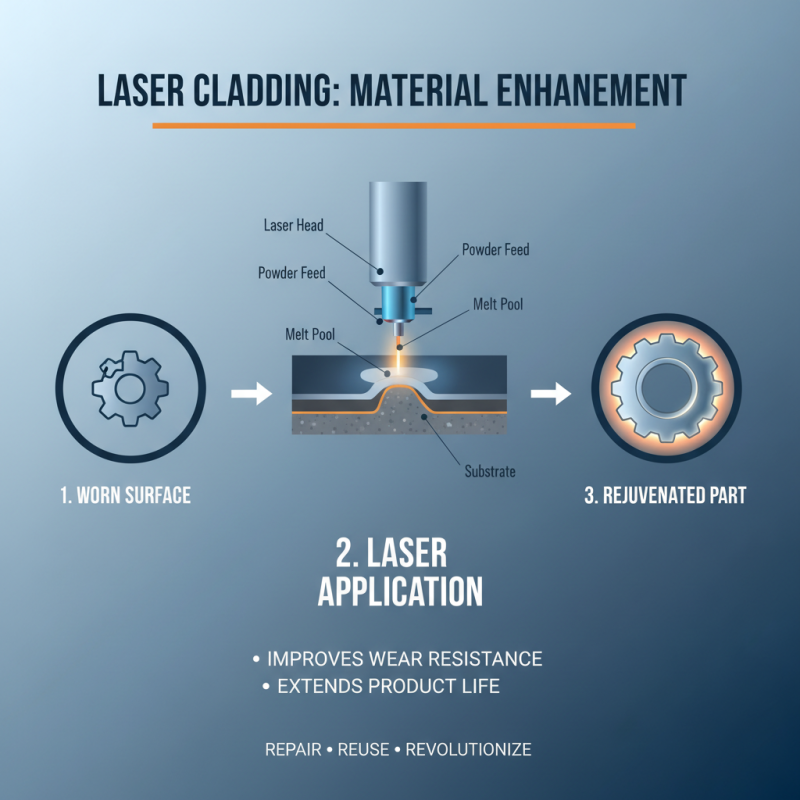
Laser cladding is a revolutionary technique in the field of material enhancement. It involves applying a layer of metal onto a substrate using a high-powered laser. This process improves wear resistance and extends product life. The importance of laser cladding lies in its capability to rejuvenate worn surfaces. It allows the repair of parts that would otherwise be discarded.
The process can be intricate. It requires precise control of laser parameters to achieve desired material characteristics. For example, too much heat can lead to warping. Conversely, insufficient heat may not bond layers properly. Understanding this balance is crucial for success. The selection of cladding materials also impacts the outcome. Not all materials combine well. Thus, list testing options and results can be fluctuating.
Moreover, the application areas are diverse. Industries benefit, from aerospace to automotive. Each sector demands specific properties, like corrosion resistance or thermal stability. Often, the choice of technique depends on the project requirements and goals. Although advancements are significant, there remain many challenges to overcome. More research is needed to refine techniques and expand their application possibilities.
Laser cladding is a sophisticated process that enhances material performance. This technique uses high-energy lasers to fuse a coating onto a substrate, improving wear resistance and surface durability. According to industry reports, laser cladding can increase the lifespan of components by up to 300%. This significant enhancement is critical in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Key principles guide effective laser cladding. The selection of appropriate powder materials is crucial. Different alloys can produce varied properties. For instance, cobalt-based powders may offer excellent corrosion resistance. The laser parameters, including power and speed, also play vital roles. Optimizing these elements ensures uniform coating and minimal distortion of the underlying material. Misalignment or improper settings can lead to defects, reminding us that precision is essential.
Another consideration is post-cladding treatment. While cladding improves surface properties, it might induce stress that can affect performance. Heat treatments may be necessary to relieve this stress. Research indicates that neglecting these steps may reduce the overall effectiveness of laser cladding. A balanced approach is necessary to achieve desired outcomes without oversights.
Laser cladding has become crucial for improving material performance in various industries. The method varies significantly, each with its distinct advantages. For example, powder feed laser cladding allows for precise control over the material thickness, making it suitable for repair applications. Reports suggest that this technique can enhance wear resistance by over 300% compared to untreated surfaces.
Wire feed cladding is another effective method. It provides lower defect rates and is generally more cost-effective. In an industry analysis, it was noted that wire feed can reduce production costs by up to 30% when applied in large-scale manufacturing. However, it may struggle with intricate geometries, leading to potential limitations in complex designs.
Another technique worth noting is direct diode laser cladding. While this method excels in speed, it can introduce challenges in material dispersion. Continuous monitoring is often required to maintain quality. Studies highlight that optimizing parameters is key, but many operators still face inconsistency issues. Therefore, mastering these various methods is essential for achieving the desired material enhancement in any project.
When evaluating laser cladding techniques, several criteria play a crucial role. The primary factors include material compatibility, deposition rate, and heat input. Each technique offers unique advantages and drawbacks. For instance, some methods yield higher deposition rates but introduce more thermal stress. Research indicates that inconsistency in heat input can lead to significant defects in the final product.
Material compatibility is another essential criterion. Different laser cladding techniques work better with specific materials. For example, some techniques can effectively bond dissimilar metals, enhancing performance. However, this can come with challenges. A study by an industry group found that nearly 30% of cladded parts fail due to inadequate bonding.
Additionally, the cost-effectiveness of each technique must be considered. While advanced methods may provide superior results, the initial investment may not be justifiable for all applications. Companies often find themselves balancing performance expectations with budget constraints. This can lead to situations where cheaper methods produce acceptable results, but also lead to long-term performance issues. Understanding these trade-offs is vital for successful laser cladding implementation.
Laser cladding technology is rapidly evolving. This process enhances material surfaces and improves performance. Researchers are exploring new methods to increase efficiency. For example, multi-layer cladding offers increased thickness and durability. New materials are also being incorporated into the cladding process. This variety allows for improved wear resistance and corrosion protection.
However, challenges remain. Not all materials bond well during cladding. Some processes result in unexpected failures. Researchers need to refine techniques to ensure better results. Additionally, more studies are required to understand the long-term effects of these treatments. This knowledge will help predict performance over time.
As developments continue, we may see advancements in automation. Automated systems can offer more precise control over the cladding process. This precision could lead to reduced waste and increased efficiency. Predictive analytics may also play a role, forecasting results based on material properties. The future of laser cladding looks promising, but there is much to consider.
| Technique | Material Types | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Laser Cladding | Metals, Alloys | High precision, minimal waste | Repair, wear-resistant coatings |
| Wire Laser Cladding | Stainless Steel, Aluminum | Continuous feed, lower cost | Additive manufacturing, surface enhancement |
| Cladding with Filler Materials | Nickel-based alloys, Tungsten | Improved corrosion resistance | Oil & gas, marine applications |
| Hybrid Laser Cladding | Cobalt alloys, Ceramics | Versatile material properties | Aerospace, automotive industries |
| Laser Cladding with Metal Matrix Composites | Composite materials | Enhanced performance, reduced weight | Transport, heavy machinery |
| Direct Energy Deposition | Titanium, Zirconium | High material deposition rate | Complex geometries, aerospace components |
| Additive Laser Cladding | Various metals, plastics | Layered production, intricate designs | Customized parts, prototyping |
| Selective Laser Melting | Nickel, Aluminum alloys | High density, excellent mechanical properties | Medical implants, aerospace |
| Laser Metal Deposition | Ferrous and Non-ferrous metals | Improved surface finish, high bonding strength | Tooling, automotive repair |
| Nanosecond Laser Cladding | Multiple materials | Minimal heat affected zone | Precision engineering, electronics |